


factory-level platform,
forging breakthroughs in speed and accuracy
Pioneering drug discovery with supercomputing integration and advanced AI, delivering a Factory-level automated platform (AI Bio-Supercom Center). Efficiently generates LaunchPad for 100+ diseases targets without interruption. LaunchPad, which is readily available ("off-the-shelf"), is being utilized to generate and validate drug candidates with the potential to obtain Investigational New Drug (IND) status.
Show More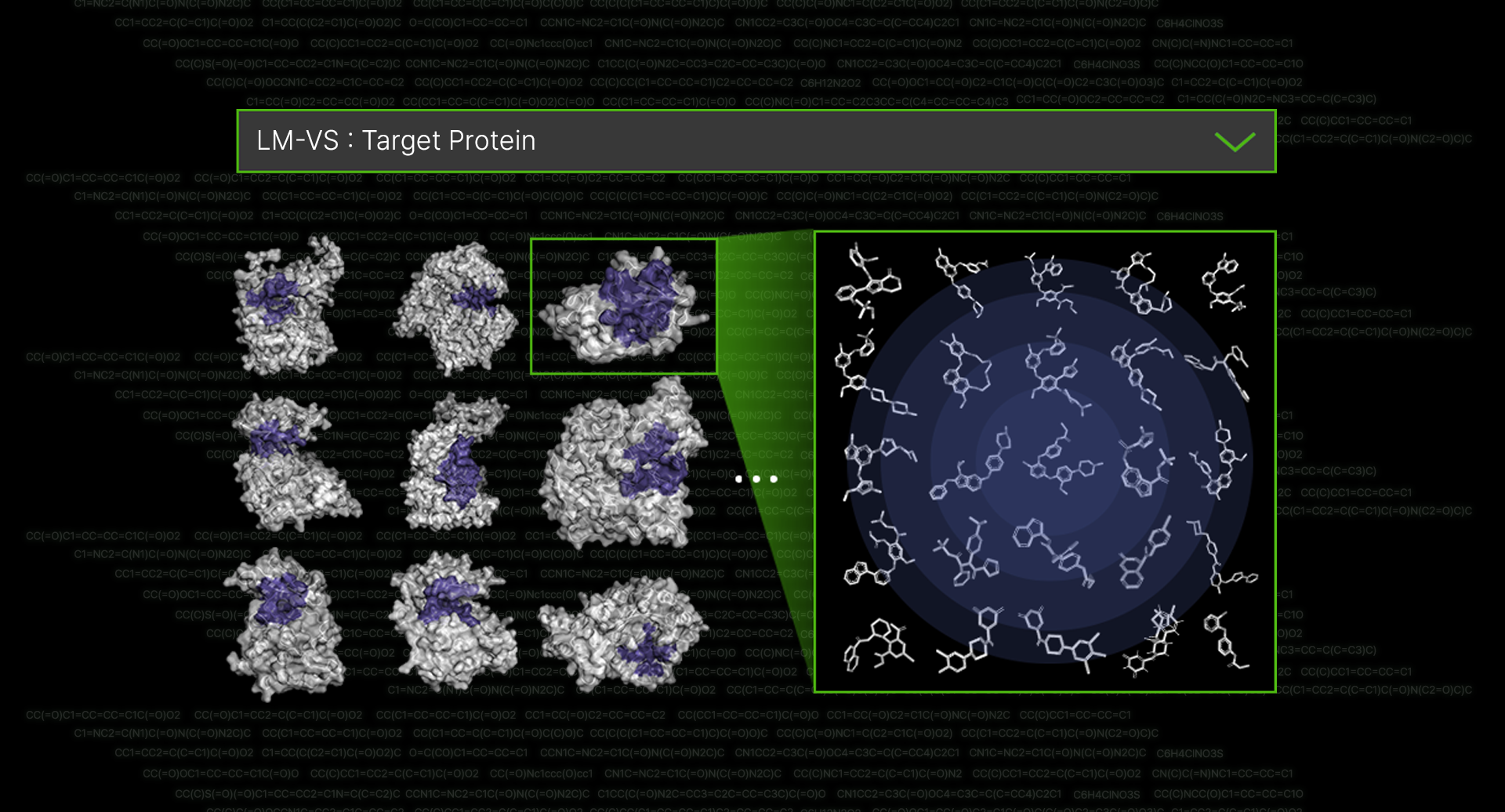

CLOUD SaaS Technology
Software as a Service (SaaS) allows researchers to concentrate on their work without the need for complex IT infrastructure, thereby expediting research progress and streamlining processes. Continual refinement of SaaS programs is essential to tackle evolving challenges and technological limitations, providing researchers with gradual enhancements that aid in their pursuit of innovative discoveries, one step at a time
Show More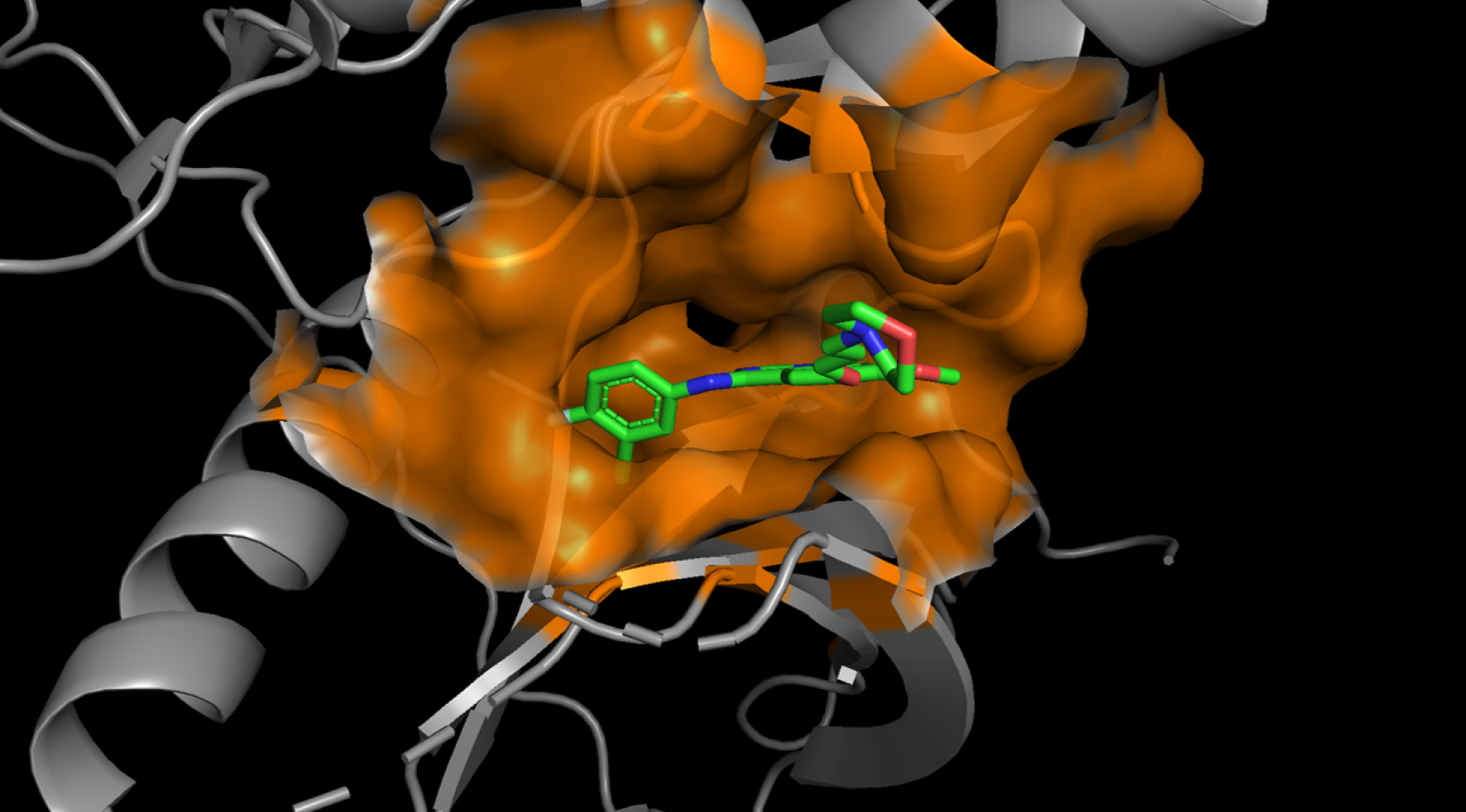
finding shortest way
Small Molecule DRUG candidate : Sm-ARS
Sm-ARS utilizes AI to predict the three-dimensional structure of protein-compound
binding, calculate binding affinities, and select optimal structures. Through molecular
dynamics simulations, thereby yielding more accurate results.
Neoantigen prediction : NEO-ARS®
AI neoantigen prediction platform integrates tumor heterogeneity and immunological knowledge,
utilizing tailored algorithms with consideration for experimental validation, capable of: 1)
developing personalized cancer vaccines, and 2) contributing to the development of universal
(off-the-shelf) cancer vaccines.
Antibody DRUG candidate : Ab-ARS®
Ab-ARS®'s CDR generator provides a solution that addresses accuracy, efficiency,
and speed issues through CDR prediction generation based on complex antibody structures
and the diversity of CDRs, while considering therapeutic efficacy.
Innovation in independent
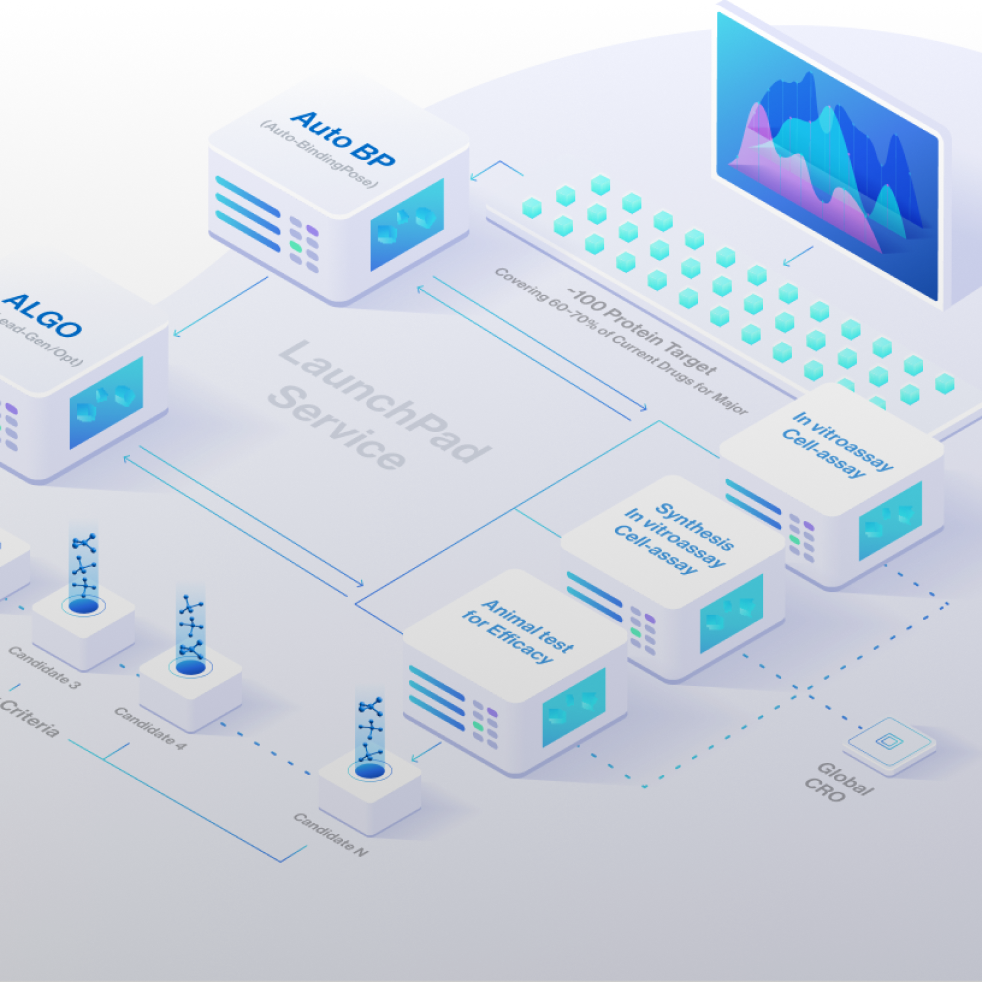
LaunchPad
One-stop-shop with technologies and services to rapidly generate and optimize drug candidates from target to IND-enabling
Pre-made Based Factory-Like Platform
Our disease-agnostic platform continuously generates a constant stream of Hits, Leads and
drug candidates that are readily available for purchase.
We also provide tailored drug discovery services.
Not Only Discovery, Add Your Choice!

SaaS
CLOUD-based AI automates drug development and genomics analysis, tailoring discoveries to customer needs.
Software as a Service
Our company has functionally segmented the entire process of AI drug development and clinical genomics analysis into step-by-step modules and created the "CLOUD-SaaS” service applying CLOUD supercomputing automation processes. Each service is readily accessible on our STB CLOUD website.

Discovery & Development
Unmatched supercomputing to support your drug discovery & development projects
Discovery & Development
This is the one-stop service based on the 'DeepMatcher®' technology. This comprehensive service, from AI-based Hit screening to preclinical candidate materials within two years, offers an end-to-end package solution, adept at addressing your challenging issues and demands to mitigate drug development risks.
Pre-made Based Factory-Like Platform
Our disease-agnostic platform continuously generates a constant stream of hits,
leads, and
drug candidates that are readily available for purchase. We also provide tailored drug discovery
services. Not Only Discovery, Add Your Choice!
Software as a Service
Our company has functionally segmented the entire process of AI drug development and clinical genomics analysis into step-by-step modules and created the "CLOUD-SaaS” service applying CLOUD supercomputing automation processes. Each service is readily accessible on our STB CLOUD website.
Discovery & Development
This is the one-stop service DDC (DeepMatcher® Drug Candidate) based on the 'DeepMatcher®' technology. This service, starting from AI-based hit screening for targets to in-vitro validation, completes the derivation of preclinical candidate substances within two years, offering a comprehensive A to Z package service.
We lead with AI and supercomputing technology
The Way of the Syntekabio
Our Archive




ABS
Supercom Center
Our established ABS center adopts state-of-the-art supercomputing technology to continuously explore new drug candidates. Through this, we provide high-quality services and products to our customers.
STB CLOUD SaaS
With excellent automation and distributed processing technology in the STB CLOUD, we can screen a library of one billion compounds.
Druggable compound
LaunchPad
The protein targets of the pre-made candidates cover 60-70% of major diseases currently under development. Syntekabio has identified over 100 targets to accelerate the discovery of new drug candidates and provide medications to more patients.
AI-automation
DeepMatcher®
Small Molecule Drug, Neoantigen, Cell therapy, Antibody Drug, Drug Repurposing, Combination Therapy, Biomarker, Clinical Genomic Analysis






